Probability Density Functions of Daily Rain
Sngequ House
See below for more information.
Description
These plots show the Probability Density Functions (PDFs) of daily total rain at stations in the UVic School-Based Weather Station Network. The blue bars give the histogram of daily rain values (greater than zero) with bins of 1 mm. The red curve is the best fit to the histogram using a three-parameter gamma function. The orange and green vertical lines give the 95th and 99th percentile respectively. The number of days of rain and the percent of the total number of events that this represents are given in the last line of the legend.
The plots are shown for the entire year and for each season. The seasons are defined as follows:
- Winter — DJF: December, January, February
- Spring — MAM: March, April, May
- Summer — JJA: June, July, August
- Autumn — SON: September, October, November
The three parameter gamma function is of the form 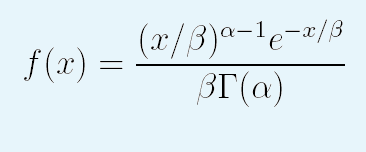
The histogram is a count of events that fall into each bin. The number in each bin is then divided by the total number events and multiplied by 100 to convert it to percent. The rain gauges can measure rain in intervals of 0.25 mm.
References
- Wilby, R.L. and T.M.L. Wigley, 2002, Future Changes in the Distribution of Daily Precipitation Totals Across North America
- Bridges, T.C. and C.T. Haan, 1972, Reliability of Precipitation Probabilities Estimated From the Gamma Distribution. Monthly Weather Review, 100, 607-611






